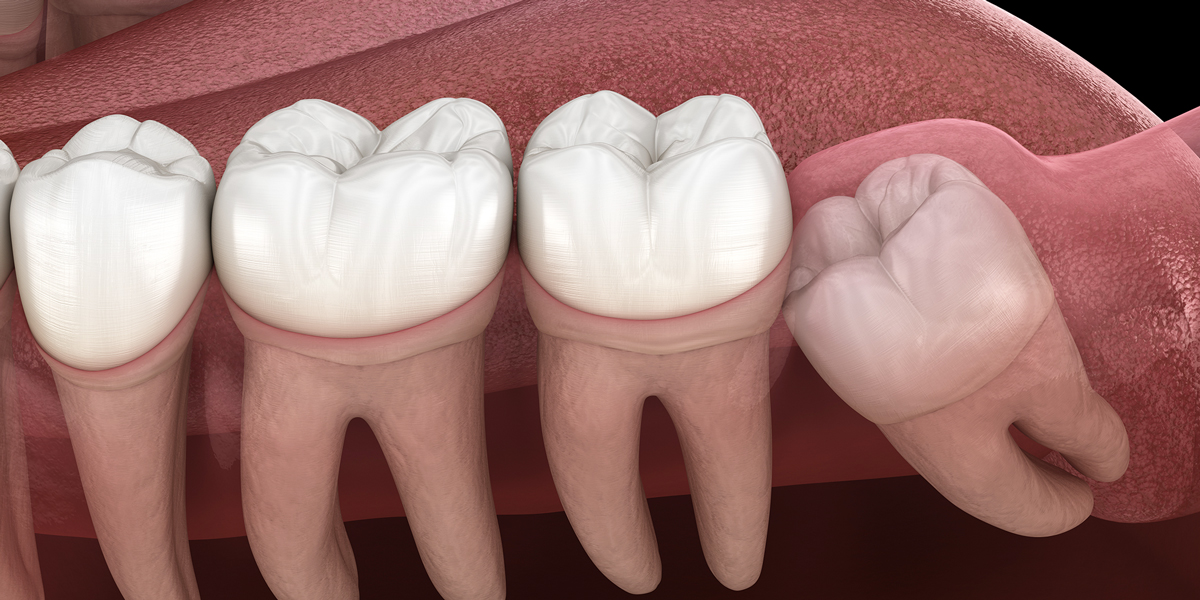
DENTAL IMPACTION
Dental impaction occurs when a tooth fails to fully emerge through the gums into its expected position in the dental arch. This condition commonly affects the third molars, also known as wisdom teeth, but can also occur with other teeth in the mouth. Impaction can result from various factors, including overcrowding of teeth, irregular tooth development, and insufficient space in the jaw.
Symptoms of dental impaction may include pain, swelling, redness, and discomfort in the affected area. In some cases, impaction may not cause any noticeable symptoms and may only be detected during a dental examination or imaging studies, such as X-rays.
Treatment for dental impaction typically involves extraction of the impacted tooth to prevent complications such as infection, damage to adjacent teeth, and misalignment of the dental arch. Depending on the position and severity of the impaction, extraction may be performed by a general dentist or an oral surgeon under local anesthesia or sedation.
In some cases, particularly with impacted wisdom teeth, extraction may be recommended even if the tooth is not causing immediate symptoms to prevent potential future problems. However, the decision to extract an impacted tooth will depend on various factors, including the patient’s age, oral health status, and the likelihood of complications.
After extraction, patients may experience some discomfort and swelling, which can usually be managed with pain medication and cold compresses. It is important to follow post-operative instructions provided by your dentist or oral surgeon to promote healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Regular dental check-ups and X-rays can help detect dental impaction early and allow for timely intervention to prevent complications. If you suspect you may have an impacted tooth or are experiencing symptoms such as pain or swelling in your mouth, schedule an appointment with your dentist for evaluation and appropriate management.
Meet Our Doctors


